# Oct 9 OSIS notes jaems ryan, ant nosaryev, evan rosenfeld fall 2025
## RISC-V (*risk-five*) crash course
## instruction types
## priveledge modes This is important since some instructions require a hart to be in a specific mode before it can be executed. some control and state registers are protected and cannot be modified in user mode, for example There are 3 modes: User, Supervisor, and Machine
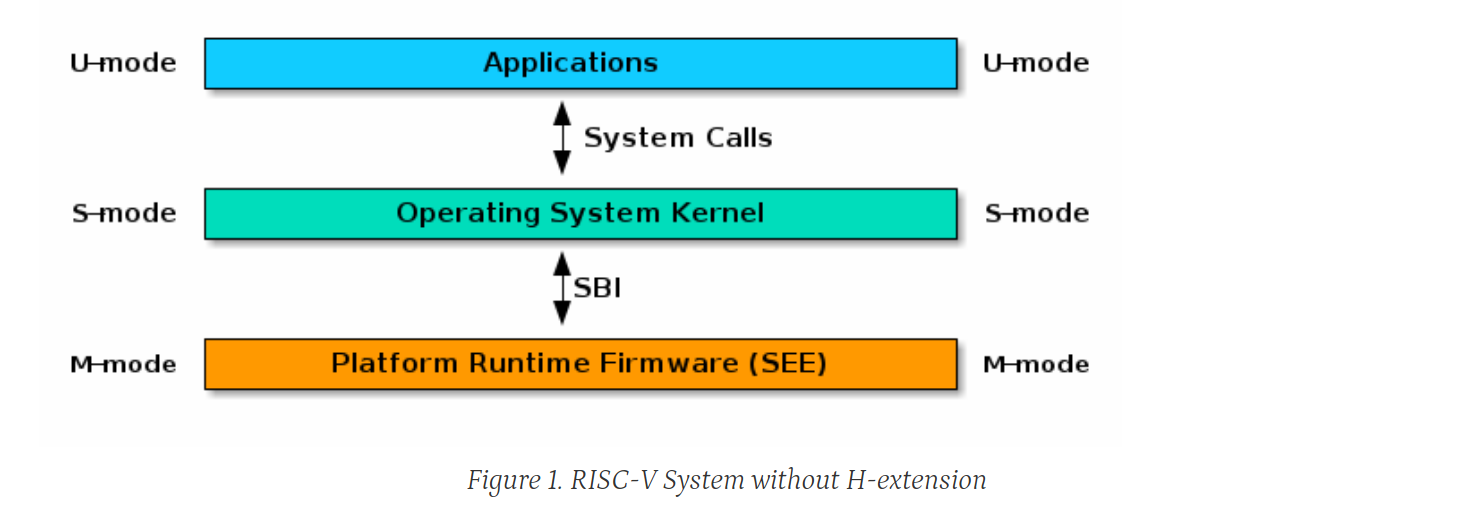 SEE - supervisor execution environment, "The SEE can be a simple boot loader and BIOS-style IO system in a low-end hardware platform" priveledged manual s1.1
From sect 1.2 of the priveleged manual: > Code run in machine-mode (M-mode) is usually inherently trusted, as it has low- > level access to the machine implementation. M-mode can be used to manage secure execution > environments on RISC-V...
> A hart normally runs application code in U-mode until some trap (e.g., a supervisor call or a timer > interrupt) forces a switch to a trap handler, which usually runs in a more privileged mode. The hart will > then execute the trap handler, which will eventually resume execution at or after the original trapped > instruction in U-mode...
> Traps that increase privilege level are termed vertical traps, while traps that > remain at the same privilege level are termed horizontal traps. The RISC-V privileged architecture > provides flexible routing of traps to different privilege layers.
Question: how do we implement this SEE & SBI to enable us to run system calls and do things from userspace?
¯\\\_(ツ)\_/¯
## model kernel [https://github.com/mit-pdos/xv6-riscv](https://github.com/mit-pdos/xv6-riscv) Used by other univertities to demonstrate OS design
## online emulator well documented and runs in a browser [https://github.com/d0iasm/rvemu](https://github.com/d0iasm/rvemu)
# roadmap
## our focus? We arent looking at any accelerator or coprocessor features. we are concerned with running code directly on a risc v core, and potentially utilizing one or more hart (thread). we may use accelerators or coprocessors for some things (I/O applications)
# next 2 weeks? 1. Read the [supervisor binary interface](https://github.com/riscv-non-isa/riscv-sbi-doc/releases/tag/v3.0) 2. Read Chapter 3 in RISC V ISA, Volume II 3. Make a repo github or git.ee.cooper.edu 4. ON an emulator (QEMU), then on the board, practice getting past the bootloader and debugging (eg, set a value in a register, and using a debug tool read the register value)